- August 12, 2024
- Posted by: Henry Wixdek
- Category: Health
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that circulates in your bloodstream and is a necessary component of cell construction and hormone synthesis. However, being vital to the body’s functioning, high cholesterol levels damage an individual’s health. In Australia, high cholesterol is a significant problem. According to the National Heart Foundation, about one-third of all Australian adults have high cholesterol and, therefore, are more exposed to threats of heart disease and stroke.
Types of Cholesterol
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Usually referred to as “bad cholesterol,” the presence of LDL cholesterol deposits cholesterol in your arteries. This plaque increases the thickness of the walls within the arteries, and the blood will not flow easily, thus raising the chances of obtaining heart disease.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): HDL is the “good” kind of cholesterol because it assists in driving the “bad” sort, LDL, from your arteries. High-density lipoprotein is known to reduce the probability of heart disease, especially when the levels of this factor are higher.
Total Cholesterol: Also called total cholesterol, this number determines the percentage of fats in the blood, including the LDL and the HDL. It needs to be monitored to gauge one’s general cholesterol situation.
Why Focus on Natural Methods?
Sustainable Long-Term Results
Naturally recommended procedures like eating right and engaging in more physical exercise aid in cholesterol reduction and attaining overall wholesome health in the long run. For instance, research in The Medical Journal of Australia explained that exercise and a diet preferred by the heart can decrease LDL cholesterol by 10% and increase the HDL cholesterol level by 5%.
How to Lower Cholesterol Naturally: Key Strategies
Heart and cholesterol health is directly determined by the proportion of nutrients of a particular type included in your diet. The following modifications to your daily diet can help you reduce cholesterol more efficiently:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Heart and cholesterol health is directly determined by the proportion of nutrients of a particular type included in your diet. The following modifications to your daily diet can help you reduce cholesterol more efficiently:
Increase Fiber Intake
Foods to Include:
Oats: Oats are also rich in soluble fibre and excellent for breakfast, whether taken in their raw state or cooked.
Barley: This grain can be consumed through soups, stews, and salads.
Beans and Lentils: These are very general and can be incorporated into place with almost any type of food.
Fruits: Both apples and pears are good examples of soluble fibre.
Why It Helps: Soluble fibre helps reduce LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often called “bad” cholesterol. It works by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and facilitating its removal from the body. According to a study from the National Heart Foundation of Australia, increasing fibre intake can reduce LDL cholesterol levels by up to 10% (National Heart Foundation of Australia, 2023).

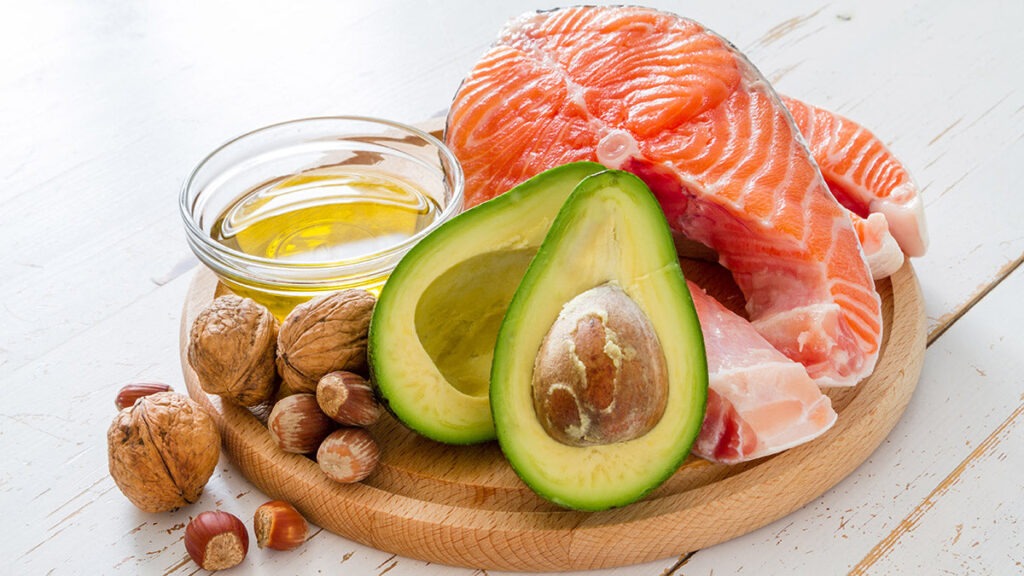
Choose Healthy Fats
Opt For:
- Avocados: It contains monounsaturated fats that are beneficial in reducing LDL cholesterol levels.
- Nuts: Nuts like almonds, walnuts, and cashews are some examples of nuts with healthy fats.
- Seeds: Jealous chia seeds and flaxseeds: you should consume them in your daily meals.
- Olive Oil: A better option than regular butter and margarine.
Limit:
- Saturated Fats: Found in red meat and many processed foods, these can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Trans Fats: Found in many fried and baked goods, trans fats raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, which is considered “good” cholesterol.
The Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend limiting saturated fat intake to less than 10% of total daily energy intake to maintain heart health (Australian Dietary Guidelines, 2020).
Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Sources:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Flaxseeds and Walnuts: Plant-based sources of omega-3s.
Benefits: Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their ability to lower LDL cholesterol and reduce inflammation. The Heart Foundation highlights that regular fatty fish consumption can decrease LDL cholesterol and improve heart health (Heart Foundation, 2023). Omega-3s also contribute to lowering triglyceride levels and supporting overall cardiovascular function.

2. Increase Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is a powerful way to manage and improve cholesterol levels. Incorporating a mix of aerobic exercise and strength training into your routine can lead to significant cardiovascular benefits and help you maintain optimal cholesterol levels.
Engage in Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise is any activity that increases your heart rate and improves circulation. It’s particularly effective for managing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health.
Examples of Aerobic Exercise
- Walking: A daily brisk walk can enhance your cardiovascular health. According to the Heart Foundation, a 30-minute walk most days can help reduce the risk of heart disease and lower cholesterol levels.
- Jogging: This high-impact activity improves cardiovascular fitness and lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol while raising HDL (good) cholesterol.
- Cycling: Whether stationary or on the road, cycling is a fantastic way to improve heart health and manage cholesterol. The Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) notes that regular cycling can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
Swimming: Swimming is a low-impact exercise that improves cardiovascular endurance and supports overall fitness. It’s also beneficial for those with joint concerns.
Recommendation:
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week. This aligns with the Department of Health guidelines, which suggest that adults should engage in regular physical activity to maintain overall health and well-being. The AIHW also supports this, highlighting that meeting these activity levels can substantially improve cholesterol and heart health.
Incorporate Strength Training
Strength training involves exercises that build muscle mass and enhance metabolic rate. This exercise is crucial in improving cholesterol levels and overall metabolic health.
Benefits
- Increases Muscle Mass: Building muscle through strength training can help improve your body’s ability to manage cholesterol and burn calories more efficiently.
- Boosts Metabolism: A higher muscle mass leads to a higher resting metabolic rate, which can aid in better cholesterol management and overall weight control.
Frequency
Include strength training exercises at least twice a week. The Heart Foundation recommends incorporating exercises that target major muscle groups to help enhance overall fitness and support cardiovascular health. This can improve your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing cholesterol levels. Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is linked to higher LDL (bad) cholesterol and lower HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Even modest weight loss can lead to significant improvements in cholesterol levels. According to the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW), losing 5-10% of your body weight can help lower LDL cholesterol and improve overall heart health.
Focus on Balanced Meals
Portion Control
Paying attention to portion sizes is fundamental to maintaining a healthy weight. Overeating, even when consuming nutritious foods, can lead to weight gain. The Australian Dietary Guidelines suggest that controlling portions helps manage energy intake and supports weight maintenance. For instance, using smaller plates or measuring food can help regulate portion sizes and prevent overeating.
Healthy Choices
Opting for balanced meals that include whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of vegetables is essential. According to Nutrition Australia, entire grains like oats and brown rice provide fibre that can help lower cholesterol. Lean proteins, such as chicken and fish, offer essential nutrients without excessive saturated fats. Vegetables, rich in vitamins and minerals, support overall health and help with weight management. The Australian Heart Foundation recommends including various vegetables in your meals to boost nutrient intake and improve heart health.
Stay Hydrated
Water Intake
Drinking sufficient water throughout the day is an often-overlooked factor in maintaining a healthy weight. Water supports numerous bodily functions, including digestion and metabolism. According to the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), the average adult should aim for about 2.6 litres of water per day for men and 2.1 litres for women. Staying hydrated helps manage appetite and supports overall health. Drinking water before meals can also help reduce calorie intake by promoting a feeling of fullness.

4. Limit Alcohol Consumption: A Key to Heart Health
Moderation in alcohol consumption plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels and maintaining overall heart health. Understanding how alcohol affects cholesterol and adhering to recommended guidelines can help you achieve a healthier lifestyle.
Guidelines for Alcohol Consumption
Men: To minimise health risks, it is advised that men limit their alcohol intake to no more than two standard drinks per day.
Women: For women, the recommendation is to limit consumption to one standard drink per day.
These guidelines are set to help mitigate the risks associated with excessive drinking, which can have detrimental effects on your heart health.
Effects of Alcohol on Cholesterol
Positive Impact: Moderate alcohol consumption may benefit your cholesterol levels. Research indicates moderate drinking can raise high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, commonly called “good” cholesterol. HDL cholesterol helps remove low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, from your bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Negative Consequences: However, the key is moderation. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to increased levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. This imbalance can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become clogged with fatty deposits, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Australian Perspective: According to the Australian Heart Foundation, excessive alcohol intake is linked to elevated cholesterol levels and other cardiovascular issues. The Foundation highlights that regular alcohol consumption can significantly impact heart health and overall well-being. To stay informed and make healthier choices, refer to resources like the Australian Government’s Department of Health for more guidelines and research.
5. Quit Smoking: A Key Step to Better Heart Health
Smoking is a significant contributor to poor cholesterol levels and heart disease. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can damage blood vessels and lower good cholesterol (HDL) levels while increasing bad cholesterol (LDL) levels. Fortunately, quitting smoking can have a profound positive impact on your cholesterol and overall heart health.
Benefits of Quitting
Improved Cholesterol Levels
One of the most significant benefits of quitting smoking is its positive effect on cholesterol levels. According to the Heart Foundation, people who quit smoking often see an increase in their HDL (good) cholesterol levels and a decrease in their LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. Studies have shown that quitting smoking can result in a 10-15% increase in HDL cholesterol levels within a few months. This improvement is crucial because higher HDL cholesterol levels help protect against heart disease.
Better Heart Health
Quitting smoking is also associated with a lower risk of heart disease. Research from the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare indicates that smokers are twice as likely to suffer from heart disease compared to non-smokers. After quitting, the risk of heart disease gradually declines, approaching the level of someone who has never smoked. Within a year of quitting, the risk of coronary heart disease can be reduced by up to 50%.
6. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress is more than just a mental burden; it can have significant repercussions on your cholesterol levels and overall health. Managing stress effectively is crucial not only for your mental well-being but also for maintaining a healthy heart. According to the Australian Heart Foundation, stress can elevate LDL cholesterol levels, often called “bad” cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease (Australian Heart Foundation, 2023).
Stress-Reduction Techniques
Exercise: Physical Activity as a Stress-Buster
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing stress and improving heart health. Regular physical activity helps release endorphins, which are natural mood lifters that can alleviate stress. The Australian Department of Health recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week (Department of Health, 2024).
Mindfulness and Relaxation: Practices for Stress Reduction
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques into your daily routine can also be beneficial for stress management. Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing help calm the mind and body, reducing stress.
Yoga, for example, has been shown to lower blood pressure and improve cholesterol levels. According to a study published in The Medical Journal of Australia, participants who practised yoga regularly experienced significant reductions in stress and improvements in their cholesterol levels (The Medical Journal of Australia, 2023). Meditation and deep breathing exercises also help lower stress by helping you focus on the present moment and alleviate anxiety.
Tracking Your Progress
Regular Check-ups
Monitoring your cholesterol levels regularly is essential for assessing the effectiveness of your lifestyle changes.
- Frequency: Aim for at least once a year or more frequently if your healthcare provider advises.
- What to Check: Total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels.
Setting Realistic Goals
- Start Small: Focus on one or two changes to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Celebrate Success: Recognise and celebrate your progress, no matter how small.
Start Your Health Journey Today!
Reducing cholesterol without medication is achievable and can be highly effective in improving your overall health and well-being. You can significantly lower your cholesterol levels by incorporating a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity, managing stress, and making other lifestyle adjustments. The Australian Pharmacy team is here to support you on this journey, providing guidance and resources to help you make informed decisions about your health. Remember, every positive change counts, and taking proactive steps towards a healthier lifestyle can lead to long-lasting benefits for your heart and overall health. If you have any questions or require personalized advice, please don’t hesitate to contact our pharmacy staff at +61 480 027 921. Your path to better health starts today!
